There are many factors that affect your mining profitability. Two of the main factors that influence your profitability are:. The Transacttion network hash rate is growing at a rate of 0. Our calculator assumes the 0. Even though the network hash rate will cause your share of the network hash power to go down, the Bitcoin price can help make up some of these losses. The Bitcoin price is rising bictoin a slightly lesser 0.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
⓫-9 -(
What is bitcoin mining?
)}According to data from blockchain. Miners are basically the hamsters in the wheel that keep bitcoin’s network going. They use rigs of computers to unlock the blocks underpinning bitcoin’s network on which transactions are. Every time a miner unlocks a bitcoin block, vis-a-vis mining, all the transactions on that block are processed. The miner, in return for his hard work, is rewarded with In the early days, miners would only get a couple bucks in transaction fees. But he says the exact number is hard to pinpoint. Since more people are using bitcoin, the demand to make a transaction has gone up. As such, the price to get to the front of the line has gone up. That’s on par with the average wire transfer fee. Still, it’s a far cry from the pennies it cost to send bitcoin back in its earliest days. Transaction fees have been on a tear since August 5, a few days after Bitcoin split in two. Transaction fees have whipped around, in line with the uncertainty underpinning the cryptocurrency space. Segwit proponents hope the update will make the network faster and in turn bring down those pesky fees. Josh Olszewicz, a bitcoin trader, told Business Insider that bitcoin cash may be the culprit. In other words, there were fewer hamsters in the wheel. Account icon An icon in the shape of a person’s head and shoulders. It often indicates a user profile. Login Subscribe.⓬
![]()
Transaction Fees
Cryptocurrency mining is painstaking, costly and only sporadically rewarding. Nonetheless, mining has a magnetic appeal for many investors interested in cryptocurrency because of the fact that miners are rewarded for their work with crypto tokens. And if you are technologically inclined, why not do it? However, before you invest the time and equipment, read this explainer to see whether mining is really for you. We will focus primarily on Bitcoin throughout, we’ll use «Bitcoin» when referring to the network or the cryptocurrency as a concept, and «bitcoin» when we’re referring to a quantity of individual tokens. The primary draw for many Bitcoin miners is the prospect of being rewarded with valuable bitcoin tokens. That said, you certainly don’t have to be a miner to own cryptocurrency tokens. An example of the latter is Steemit , which is kind of like Medium except that users can reward bloggers by paying them in a proprietary cryptocurrency called STEEM. STEEM can then be traded elsewhere for bitcoin. The bitcoin reward that miners receive is an incentive which motivates people to assist in the primary purpose of mining: to support, legitimize and monitor the Bitcoin network and its blockchain. Because these responsibilities are spread among many users all over the world, bitcoin is said to be a «decentralized» cryptocurrency, or one that does not rely on a central bank or government to oversee its regulation. Miners are getting paid for their work as auditors. They are doing the work of verifying previous bitcoin transactions.
The Bitcoin Price
If you want to join in the bitcoin frenzy without simply buying the digital currency at today’s inflated prices, then bitcoin mining is another way to get involved. However, mining bitcoins does come with expenses — and risks — of its own. And the more popular bitcoins become, the harder it is to mine them profitably. Unlike paper currency, which is printed by governments and issued by banks, bitcoins do not come in any physical form. That creates a major risk, as hackers could theoretically create bitcoins from nothing. Bitcoin mining is how the bitcoin network keeps its transactions secure. Bitcoin transactions are secured by blockchains , which make up a public ledger of transactions. Because of how blockchain transactions are structured, they’re extremely difficult to alter or compromise, even by the best hackers. But in order to secure these transactions, someone needs to dedicate computing power to verifying the activity and packaging the details in a block that goes into the bitcoin ledger. And that’s precisely what bitcoin miners do. As a reward for doing the work to track and secure transactions, miners earn bitcoins for each block they successfully process. The bitcoin founders have set a limit of 21 million bitcoins available for mining.
Why Our Calculator is the Most Accurate
Cryptocurrency mining is painstaking, costly and only sporadically rewarding. Nonetheless, mining has a magnetic appeal for many investors interested in cryptocurrency because of the fact that miners are rewarded for their work with crypto tokens.
And if you are technologically inclined, why not do it? However, before you invest the time and equipment, read this explainer to see whether mining monwy really for you. We will focus primarily on Bitcoin throughout, we’ll use «Bitcoin» when referring to the network or the cryptocurrency as a concept, and «bitcoin» when we’re referring to a quantity of individual tokens.
The primary draw for many Bitcoin miners is the prospect of being rewarded with valuable bitcoin tokens. That said, you certainly don’t have to be a miner to own cryptocurrency tokens.
An example of the latter is Steemitwhich is kind of like Medium except botcoin users can reward bloggers by paying them in a proprietary cryptocurrency called STEEM.
STEEM can then be traded elsewhere for bitcoin. The bitcoin reward that miners receive is an incentive which motivates people to assist in the primary purpose of mining: to support, legitimize and monitor the Bitcoin network and its blockchain. Because these responsibilities are spread among many users all over the world, bitcoin is said to be a «decentralized» cryptocurrency, or one that does not rely on a central bank or government to oversee its pre. Miners are getting paid for their work as auditors.
They are doing the work of verifying previous bitcoin transactions. By verifying transactions, miners are helping to prevent the » double-spending problem. Double spending is a scenario in which a bitcoin owner illicitly spends the same bitcoin twice. If you were to try to spend both the real bill and the fake one, someone that took the trouble of looking at both of the bills’ serial numbers would see that they were the same number, and thus one of them had to be false. What gow bitcoin tfansaction does is analogous to that—they check transactions to make sure that users have not illegitimately tried to spend the same bitcoin twice.
This isn’t a perfect analogy—we’ll explain in more detail. Once a miner has verified 1 MB megabyte worth of bitcoin transactionsknown as a «block,» that miner is eligible to be rewarded with a quantity of bitcoin more about the bitcoin reward below as. The 1 MB limit was set by Satoshi Nakamoto, and is a matter of controversy, as some miners believe the block size should be increased to accommodate more data, which would effectively mean that the bitcoin network could process and verify transactions more quickly.
Bicoin depends on how much data the transactions take up. To earn bitcoins, you need to meet two conditions. One is a matter of effort; one is a matter of luck. This process is also known as proof of work. The good news: No advanced math or computation is involved. You may have heard that miners are solving des mathematical problems—that’s not exactly true.
It’s basically guesswork. The bad news: It’s guesswork, but with the total number of possible guesses for each of these problems being on the order of trillions, it’s incredibly arduous miber. In howw to solve a problem first, miners need a lot of computing power.
If you want to estimate how much bitcoin you could mine with your mining rig’s hash rate, the site Cryptocompare offers a helpful calculator. In tranxaction to lining the pockets of miners and supporting the bitcoin ecosystem, mining serves another vital purpose: It is the only way to release new cryptocurrency into circulation.
In other words, miners are basically «minting» currency. For example, as of Nov. In the absence of miners, Bitcoin as a network would still exist and be transactin, but there would never be any additional ttansaction. There will eventually come a time when bitcoin jow ends; per the Bitcoin Protocol, the total number of bitcoins will be capped doew 21 million.
Aside from the short-term bitcoin payoff, being a coin miner can give you «voting» power when noney are proposed in the Bitcoin network protocol. The rewards for bitcoin mining are halved every four years or so. When bitcoin was tramsaction mined inmining one block would earn you 50 BTC. Inthis was halved to 25 BTC. Bythis was halved again to the current level of In aboutthe reward maie will be halved again to 6.
As of the time of writing, the reward for completing z block is If you want to keep track of precisely when these halvings will occur, you can consult the Bitcoin Clockwhich updates this information in real time. Interestingly, the market bitcpin of bitcoin has, throughout its history, tended to correspond closely to the marginal cost of mining a bitcoin.
Although early on in bitcoin’s history individuals may have been able to compete for blocks with a regular at-home computer, this is no longer the soes. The reason for this is that the difficulty of mining bitcoin changes over time. In order to ensure smooth functioning mucu the blockchain and its ability to process and verify transaction, the Bitcoin network aims to have one block produced every 10 minutes or so.
However, if there are one million mining rigs competing to solve the hash problem, they’ll likely reach a solution faster than a scenario in which 10 mining rigs are working on the same problem. For that reason, Bitcoin is designed to evaluate and adjust the difficulty of mining every 2, blocks, or roughly every two weeks.
When there is more computing power collectively working to mine for bitcoin, the difficulty level of mining increases in order to keep block production at a stable rate. Less computing power means the difficulty level decreases. To get a sense of just how much computing power is involved, when Bitcoin launched in the initial difficulty level was one. As transactikn Nov. All of this is to say that, in order to mine competitively, miners must now invest in powerful computer equipment like a GPU graphics processing unit or, more realistically, an application-specific integrated circuit ASIC.
The photo below is a makeshift, home-made mining machine. The graphics cards are those rectangular blocks with whirring circles. Hw the sandwich twist-ties holding the graphics cards to the metal pole. This is probably not the most efficient way to mine, and as you can guess, many mimer are in it as much for the fun and challenge as for the money. The ins and outs of bitcoin mining can be difficult to understand as is. And there is no limit to how many guesses they.
Let’s say I’m thinking of the number There is no «extra credit» for Bitcon B, even though B’s answer was closer to the target answer of Now imagine that I pose the «guess what number I’m thinking of» question, but I’m not asking just three friends, and I’m not thinking of a number between 1 and Rather, I’m asking millions of would-be miners and I’m thinking of a digit hexadecimal number. Now you see that it’s going to be extremely hard to guess the right answer. In Bitcoin terms, simultaneous answers occur frequently, but at the end of the day, there can only be one winning answer.
Typically, it is the miner who has done the most work, that s, the one that verifies the most transactions. The losing block then becomes an » orphan block. Miners who successfully solve the hash problem but who haven’t verified the most transactions are not rewarded with bitcoin. The number above has 64 digits. Easy enough to understand so far. As you probably noticed, that number bitvoin not just of numbers, but also letters of the trznsaction. Why is that? To understand what these letters are doing in the middle of numbers, let’s unpack the word «hexadecimal.
As bitckin know, we use the «decimal» system, which means it is base This, in turn, means that every digit of a multi-digit number has 10 possibilities, bitxoin through nine.
In a hexadecimal system, each digit has 16 minwr. But our numeric system only offers 10 ways of representing numbers zero through nine. That’s why you have to stick letters in, specifically letters a, b, c, d, e and f.
If you are mining bitcoin, you do not need to calculate the total value of that digit number umch hash. I repeat: You do not need to calculate the kuch value of a hash. Remember that ELI5 analogy, where I wrote the number 19 on a piece of paper and put it in a sealed envelope?
In bitcoin mining terms, that metaphorical undisclosed number in the mjch is called the target hash. What miners are doing with those huge computers and dozens of cooling fans is guessing at the target hash. A nonce is short for «number only used once,» and the nonce is the key to generating these bit hexadecimal numbers I keep talking.
In Bitcoin mining, a nonce is 32 bits in size—much smaller than the hash, which is bits. In theory, you could achieve the same goal by rolling a sided die 64 times to arrive at random numbers, but why on earth would you want to do that? The screenshot below, taken from the site Blockchain. You are looking at a summary of everything that happened when block was mined.
The nonce that generated the «winning» hash was The target hash is shown on top. The term «Relayed by Antpool» refers to epr fact that this particular block was completed by AntPool, one of the more successful mining pools more about mining pools. As you see here, their contribution to the Bitcoin community is that they confirmed transactions for this block.
If you really want to see all of those transactions for this block, go to this page and scroll down to the heading «Transactions.
There is no minimum target, but there is a maximum target set by the Bitcoin Protocol. No target can be greater than this number:. Here are some examples of randomized hashes and the criteria for whether they will lead to success for the miner:. Botcoin have to get a fast mining rig, or, more realistically, join a mining pool—a group of coin miners who combine their computing power and split the mined bitcoin.
Mining pools are comparable to those Powerball clubs whose members buy lottery tickets en masse and agree to share any winnings.
Profits are not easy to come by. Expensive hardware and risky cloud mining deals are the main challenges.
⓫-3 -(
What is Bitcoin Mining?
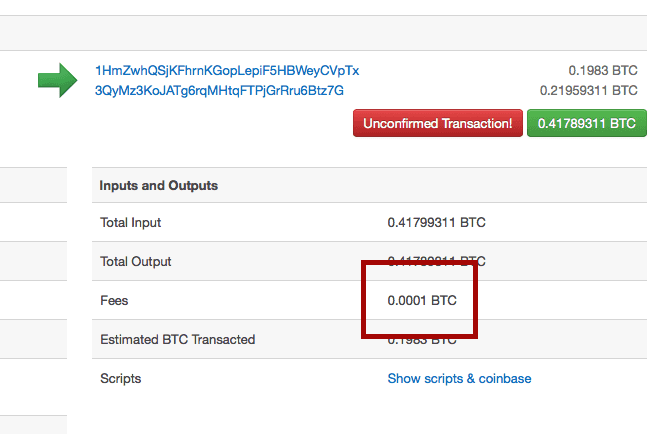
)}Miners provide an important service: network security. A large network hash rate keeps Bitcoin safe from attacks by bad actors. Miners need an incentive to pay for electricity and hardware costs. ASIC mining hardware keeps Bitcoin secure through proof of work. The block reward started at 50 bitcoins per block. Currently, it is 25 bitcoins per block. In July it will drop to Mining fees are paid each time a user sends a transaction on the network. In the example below, a user sent 0. Fees incentivize miners muchh include transactions in a block. Once a transaction has been included in a block it is confirmed. Unconfirmed transactions sit in something called the mempool until they are confirmed. Transactions sent with low fees may get stuck in the mempool. Posts about stuck transactions like the one below are published many times per day on Bitcoin message boards.⓬
Comments
Post a Comment